Molecular structure of AKD sizing agent
AKD sizing mechanism
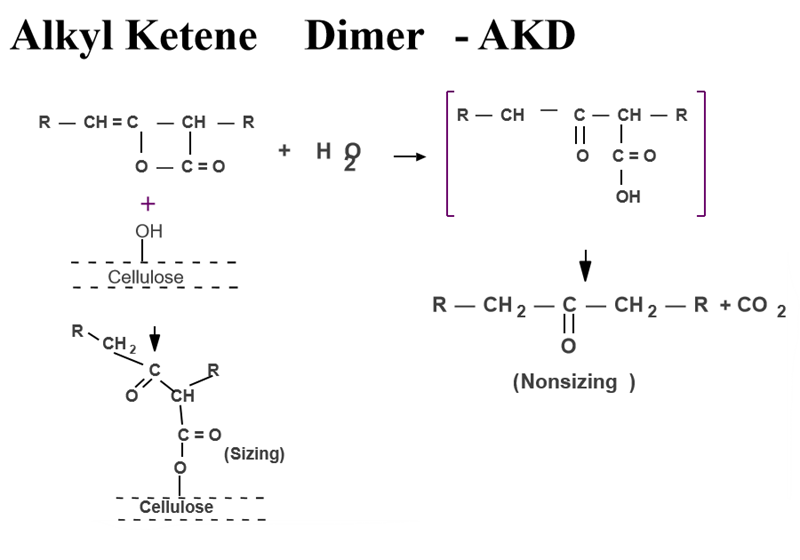
AKD sizing reaction three stages
1. AKD is electrostatically adsorbed to the fiber, and the cationic starch plays a supporting role.
2. The paper sheet is heated and dried, and the AKD melts and expands to form a film covering the paper surface.
3. The AKD molecules begin to rearrange when heated, repelling water and giving the paper water-resistant properties. The aging reaction continues during rewinding and storage.
The reaction between AKD and fiber cannot proceed significantly until most of the moisture in the paper is evaporated. Depends on system pH, alkalinity and temperature.
Stage 1: Retention and Integration
AKD Dimer is made into a stable emulsion. The AKD emulsion particles are combined with the fiber surface due to the action of charge. The adding position of AKD emulsion and the order in which it is added with other chemicals have a great influence. The retention scheme can retain fillers, small fibers and AKD
If AKD cannot be retained, hydrolysis problems will occur.
Stage 2: Distribution
If it is retained on the fiber surface in the form of particles, its coverage area will be very limited. The better the coverage effect of AKD on the fiber surface, the better the gluing effect of the paper. The influence of dry operating conditions on the gluing effect of AKD Very large, and in some cases, the distribution reaction step of this AKD will be the most influential operation.
Stage 3: Reaction
Not all AKD can react with fiber. Unreacted AKD sizing agent can only reach 20~30% of the efficiency of reacted AKD sizing agent. This reaction stage has a great influence on the development of AKD sizing effect.
Two important factors affecting AKD
poor retention
AKD will be adsorbed on fillers and fine fibers, but it is not easy to effectively retain on paper. When it enters white water, AKD will undergo a hydrolysis reaction due to pH value, temperature and time conditions. When it has a chance to be retained again, it has lost part or all of its gluing function.
Fillers that adsorb AKD flocculate due to retaining additives
After the filler adsorbing AKD is flocculated, most of the sizing agent is trapped inside the flocculated filler, and it cannot expand to cover the fibers and react with the fibers during the drying stage. The surface of PCC has many microporous structures, and AKD will be absorbed and affect the strength of the glue.
It needs to be emphasized that the gluing effect of AKD depends critically on the retention system, and the optimization of the entire retention system is often more important than the selection of AKD varieties.
Increase the bonding between AKD sizing agent and fiber
Use more starch
Use glue accelerator
Control reasonable drying temperature and moisture content
Change fiber surface properties
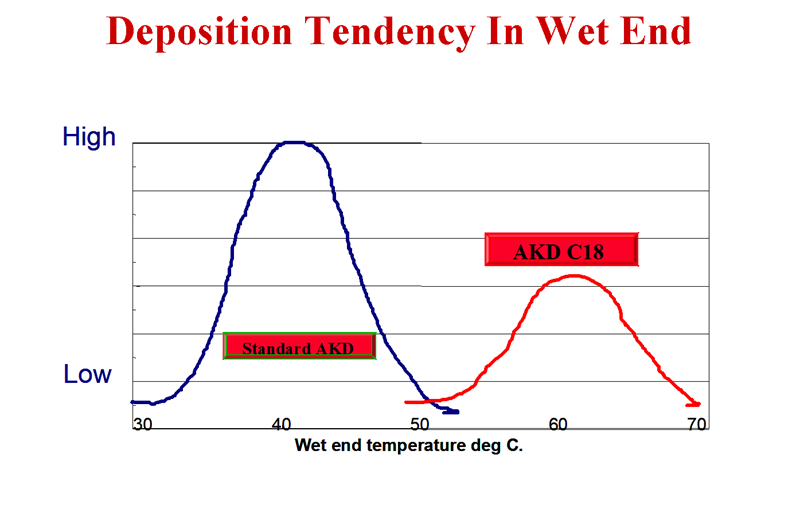
Deposition trend at the wet end

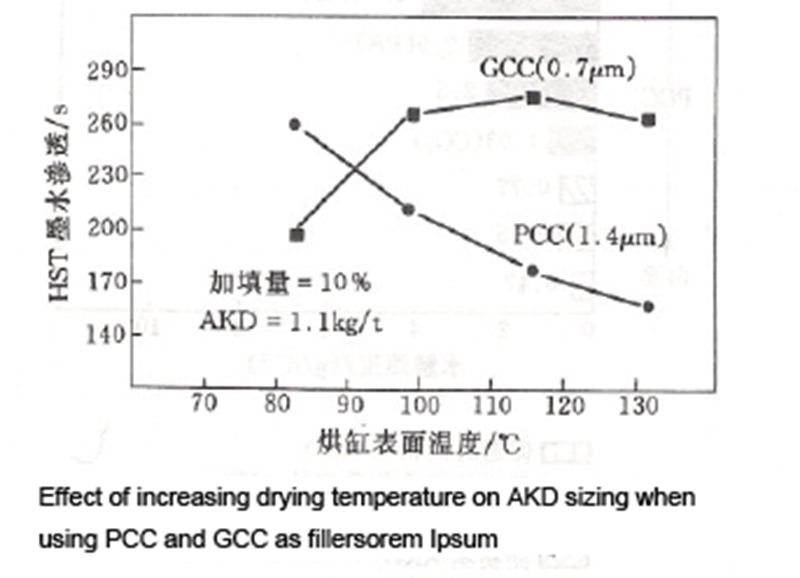
The influence of calcium carbonate filler on AKD sizing
Various types of AKD hydrolysis
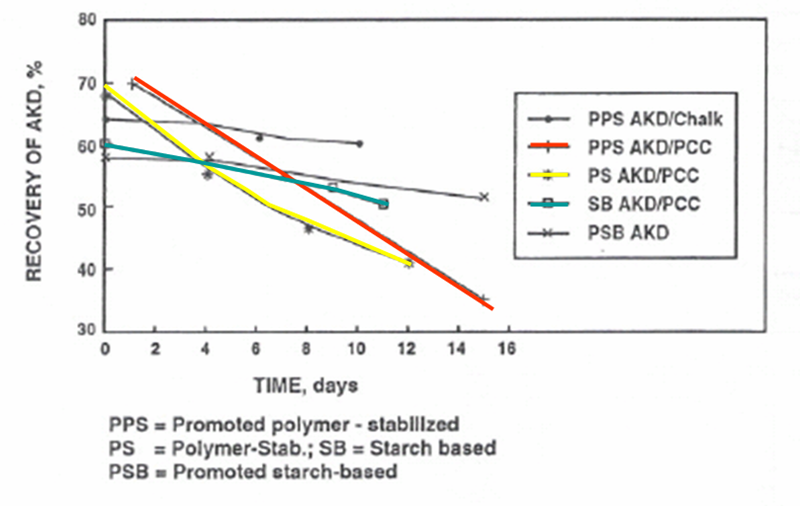
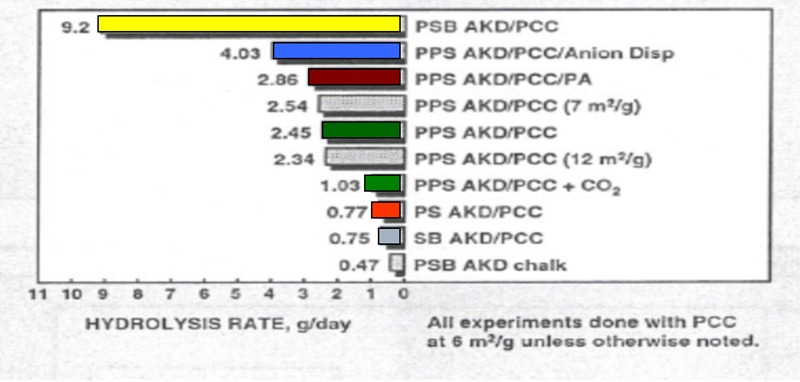
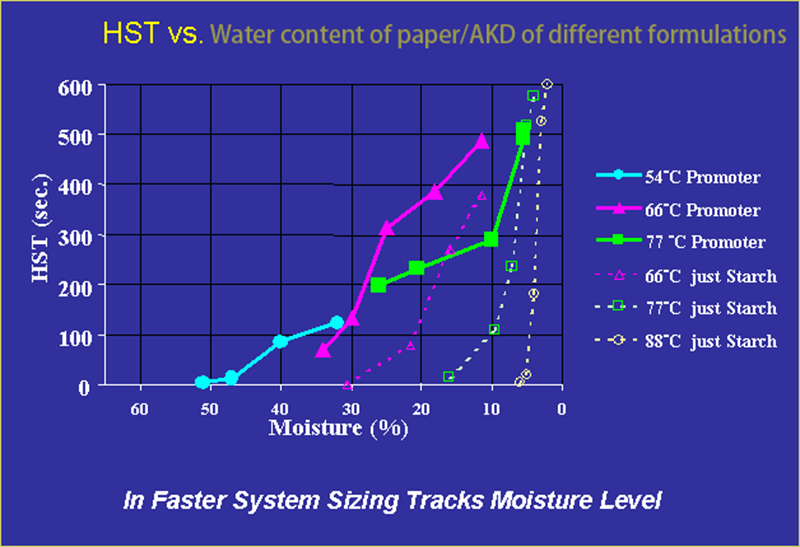
Effect of paper moisture on sizing
Optical brightener OBA
The presence of sulfonic acid groups makes OBA anionic, and the fiber surface is negatively charged. It is difficult to attach to the fiber surface due to homogeneous electrical repulsion. Ca2+ and Mg2+ in water can reduce the electric repulsion reaction.
1. Surface sizing is cheaper than using OBA in the wet end and has good distribution.
2. OBA in paint requires adhesives to improve its effect. Good adhesives include starch and cheese.
Protein, carboxymethyl cellulose CMC, polyvinyl alcohol PVA
3. Low PH and Al3+ damage the whitening effect of OBA
Effect of surface gum starch on AKD
PH value – maintain the range of 7.0~9.0, too low will affect AKD maturation, too high will destroy AKD bonding
The source of the ammonia component – it is an effective base, which will penetrate and destroy the lipid bond between AKD and fibers. (AP)
Additives – ammonia-generating substances, pH adjusters, starch oxidizers, etc.
Effective AKD content – maintain a portion of the effective AKD content to react with the surface gumming starch post-machine to produce sufficient gumming.
Starch reflux – If the quality of the starch liquid will affect the AKD sizing effect, the amount of reflux
The more there are, the greater the impact.
Starch cooking – excessive conversion will greatly increase the content of Amylose, and the Amylose will become
The chance of reaction with AKD will be greatly increased, and the water-repellent hydrocarbon chain on the AKD structure will be wrapped into a helical
The water resistance of Amylose molecules is significantly reduced.
PH vs Alkalinity
Alkalinity refers to the ability of a sample to donate hydroxyl ions to water, or is a measure of the water’s ability to accept protons. Carbonates, bicarbonates, hydroxides, borates, silicates, and phosphates all have the ability to provide hydroxide ions to water. Calcium carbonate is an alkaline filler commonly used in the wet end of papermaking and has an important impact on the alkalinity of paper stock.
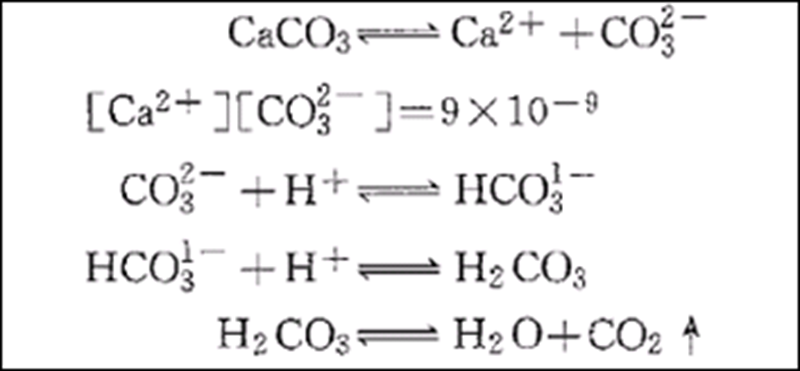
Controlling the alkalinity of the water system is more important in rosin-aluminum sulfate sizing and AKD neutral sizing than controlling the pH value of the system.
Effect of pH on AKD reaction
The sizing performance of AKD is closely related to the pH value. It is generally believed that only under neutral/alkaline conditions can the lactone ring of AKD open and react with the hydroxyl groups on cellulose.
Experiments have shown that when the pH is less than 6.0, AKD can hardly produce sizing effects. As the pH value increases, the sizing efficiency of AKD will gradually increase, especially when the system pH value is between 6.5-7.5, the paper sizing degree increases fastest. However, when the system pH value is greater than 8.0, the rate of increase in sizing begins to slow down.
There is another possibility that the pH value affects the sizing performance of AKD, that is, the pH value affects the ionization of the carboxyl group. Since the carboxyl group is the main retention point of AKD and other cationic wet-end additives, at a lower pH value, almost all carboxyl groups are protonated, and the surface charge of fibers and fine fibers is almost zero, which is not conducive to the retention of AKD on the fiber surface. As the pH value increases, the carboxyl groups are gradually ionized, the negative charge on the fiber surface gradually increases, and more and more AKD remains on the fiber surface. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) can improve the sizing effect of AKD. There are two possibilities. One is that (HCO3-) can enhance the retention of AKD on the fiber surface. Another possibility is that (HCO3-) can enhance the swelling of the fiber, so that the cellulose hydroxyl groups are fully exposed, which is conducive to the reaction of AKD with it.
How to improve the aging rate of AKD
Rapid heating
The more water is removed from the pressing section
The higher the drying temperature
Extended drying time
The number of high-temperature drying cylinders
High-temperature initial roll paper
The effect of temperature on AKD aging
The temperature of the drying section is full width
The temperature of the paper roll at the initial roll machine position
The interval between the large paper roll of the initial roll machine and the rewinder
Natural aging
The effect of the drying process on AKD sizing
If the water content of the lower machine is constant, in order to obtain the best sizing degree, the minimum drying cylinder can be used to ensure that the temperature of the last drying cylinder is as high as possible.
If the dryer cannot be shut down, the steam flow to the front dryer can be reduced to allow the paper to reach the maximum temperature in the back dryer.
Reducing the moisture content of the bleached kraft pulp (blank dry, if possible) will reduce the absorption, regardless of the size grade. The additional steam is offset by the steam savings in the back dryer.
Typical board machine dryer section temperatures
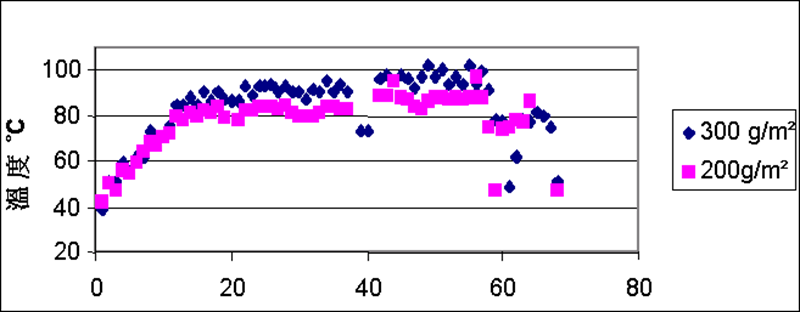
Effect of steam dosage on the temperature of paperboard at the rear end of the drying cylinder section

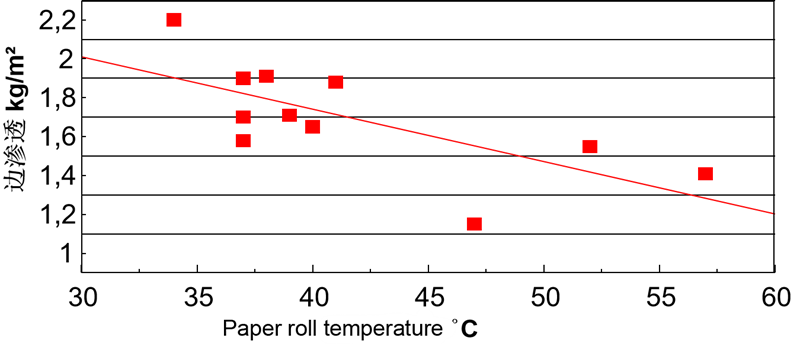
Effect of Paper Roll Temperature on Edge Penetration
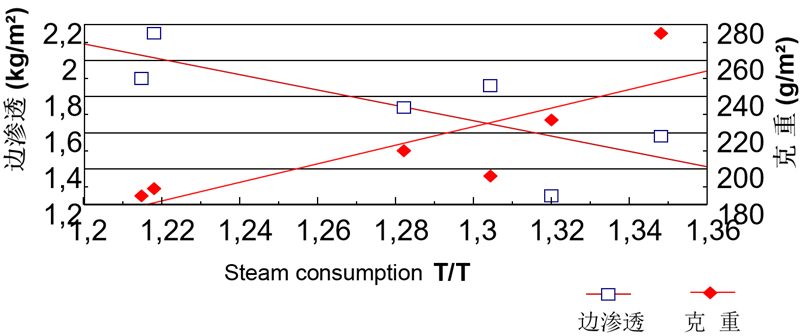
Effect of gram weight and steam dosage on edge penetration
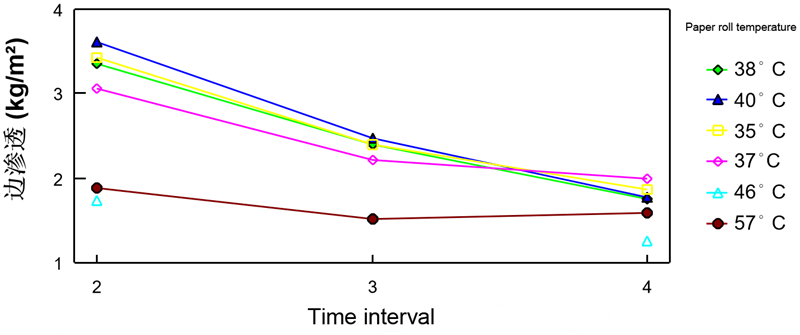
AKD natural aging glue strength under different paper roll temperature conditions
Melting point and crystallization temperature

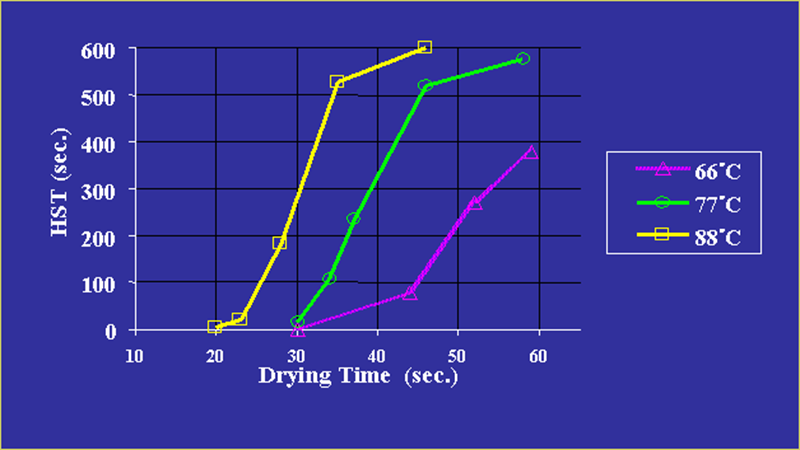
Effect of drying temperature on AKD reaction rate With starch and without promoter resin
AKD sizing agent sizing degradation problem,The gluing strength of paper decreases with time.
AKD上胶剂的上胶退化问题
Causes of glue degradation
1. Newly exposed fiber surface
High humidity and high temperature storage environment
Contact with vapors of other polarities
2. The reaction completes the rupture of the sizing agent
UV light exposure
Ammonia vapor
high pH
3. Degradation of unreacted sizing agent
PCC precipitated calcium carbonate
Moisture
Alkali component
How to avoid or reduce glue degradation problems
The adding points of sizing agent and filler should be separated
Use glue accelerator
Add single ingredients or add separately
PAE=DicyDADMAC>>>DMA/epi
Increase the amount of sizing agent
Use fillers with low quicklime content
Use low specific area fillers
Avoid storing paper in undesirable conditions
High temperature and high humidity conditions
Do not expose to UV light
Reduce the use of wetting agents
Factors affecting AKD maturation
The difficulty of sizing paper pulp
For pulps such as groundwood pulp that are difficult to glue, the reaction between the sizing agents is very slow, so the gluing and maturation speed will not be as good as that of unbleached kraft pulp that is easy to glue.
Pulp pH during pulping process
If the pulp reacts at a high pH value during the pulping process, the pulp fibers will absorb alkalinity into the internal structure of the fibers, giving the fibers good gluing and maturing rates.
pH value of pulp during storage
If the pulp is stored at a high concentration, its pH value will be high.
The pulping process is operated under high pH conditions, so the pulp fiber will have good gumming and maturing rate due to the absorption of alkalinity.
If the pH value in the paper machine system is high, the curing rate will be high.
If the alkalinity in the paper machine system is high, the curing rate will be higher.
Factors affecting AKD maturation
The primary retention rate will affect the curing rate. If the retention rate is not good, more sizing agent will be distributed on the carpet surface (double mesh will be on the middle layer), resulting in poor glue on the mesh surface, or uneven appearance on both sides. best situation.
Surface gluing tests, such as; water drop/Cobb/contact angel test results on the mesh surface will not be good, but as time goes by, the AKD on the carpet surface will transfer to the mesh surface and the mesh surface will be glued The degree increases, and this phenomenon will be more obvious for systems with low AKD dosage.
Penetrating gluing test, such as HST/ink float, etc., the gluing test results may be very good, because the sizing agent concentrated in a certain paper layer will form a strong water-resistant layer to prevent the penetration of liquid. In this case It is especially obvious in low-weight paper. However, if the sizing curing rate of this type of paper is not ideal, the sizing test will show poor results due to the transfer of sizing agent. This phenomenon will be more obvious for systems with low AKD dosage.
For multi-layer paperboard, the amount of AKD in a single layer will affect the gluing degree of the paper layer, because AKD will transfer from the paper layer with high AKD retention to the paper layer with low retention, and the final gluing degree will be lower than the original one. Glue level is low.
The use of low molecular weight polyDADMAC will increase the sizing degree of AKD on the paper machine. Because the curing rate on the paper machine is high, the curing rate of AKD in the future will show a lower result.
A special low molecular weight coagulant – DMAepi was found to cause the degradation of AKD sizing, while other coagulants did not have this phenomenon.
If the paper contains a high moisture content during the drying process, AKD will be partially hydrolyzed. If the moisture content of the paper is low, the gluing and maturation of the paper will be better. If the moisture content of the paper is high, the AKD will be partially hydrolyzed during the rapid drying process. A higher amount of AKD produces a hydrolysis reaction, so its sizing curing rate is poor. If the paper with lower moisture content and high AKD content is dried under high-speed drying conditions, the results will be exactly the opposite, and better on-machine results will be obtained. Glue maturation effect.
Adding high-surface-area fillers will lead to a deterioration of the AKD curing rate on the machine and will cause the degradation of the glue. In the early stages of glue application, AKD covering the surface of the filler can provide a temporary glue effect, but over time Extended, because this AKD cannot effectively react with fiber, but will react with water to produce hydrolysis. Of course, this can be achieved by increasing the amount of AKD to achieve the necessary gluing degree, but generally speaking, the efficiency will be poor. The situation is particularly serious in systems using PCC calcium carbonate.
High temperature drying can increase the AKD curing rate on the machine.
If there is starch surface gluing treatment equipment on the machine, the AKD gluing effect on the machine will be reduced, because the hydrophilic group on the starch will cover the hydrophobic group on the AKD, but the unreacted AKD will be transferred to the starch layer and cause It has a gluing effect, which gives it a post-machine gluing and aging effect. This phenomenon is more obvious for systems with high AKD dosage.
There is a more special example: if you use starch with a high linear amylose content or a starch with a high oxidation rate, the helical structure between the starch molecules will cover the water-repellent group on the AKD structure, resulting in a reduction in the curing rate after the AKD machine. Or stop altogether.
Calendering of dried paper will destroy the structure of the paper and produce a lot of unglued paper fibers. As time goes by, AKD will transfer to the unglued fibers. This situation is more obvious for systems with high AKD. .
Paper with a low moisture content will have a better on-machine gluing and curing rate, but its post-machine curing rate will be poor.
If the temperature of the paper roll in the coiler is high enough, it will be helpful for the AKD curing effect. If there is a heating device at the calender, it will be helpful for gluing, and if the opening between the calender and the coiler is The shorter spatial distance improves the curing effect of the glue on the paper roll because the paper is able to retain its temperature.
The time between winding and rewinding the finished product is about 20 minutes to 1.5 hours. The difference in this time will produce different product gluing results, because AKD will have more time to gluing in the winding paper roller that is still warm. reaction.
The temperature of the paper on the rewinder will affect the final gluing quality of the paper. This effect is related to the operating speed of the rewinder. If the rewinder uses an unwinding roller, the temperature of the paper will increase. As long as these operating factors can prevent the decrease of the paper temperature , then it is a favorable factor for AKD gluing.
Different numbers of rewinding small paper rolls will have different glue levels because their AKD curing times are different.



